DNS Lookup Explained: How Domain Name System Works to Connect You to Websites Fast
Created on 9 October, 2025 • Checker Tools • 101 views • 2 minutes read
What is DNS Lookup? The internet runs on a vast system that connects billions of devices worldwide. Yet, most users don’t realize how this connection happens every time they visit a website
What is DNS Lookup?The internet runs on a vast system that connects billions of devices worldwide. Yet, most users don’t realize how this connection happens every time they visit a website. DNS Lookup (Domain Name System Lookup) is the hidden process that translates a domain name like www.example.com
into an IP address that computers understand. Without DNS, users would have to remember complex strings of numbers instead of simple names.
Essentially, DNS acts like the phonebook of the internet. When you type a website’s name in your browser, your computer performs a DNS Lookup to find the correct IP address and establish a connection with the web server.
How DNS Lookup Works
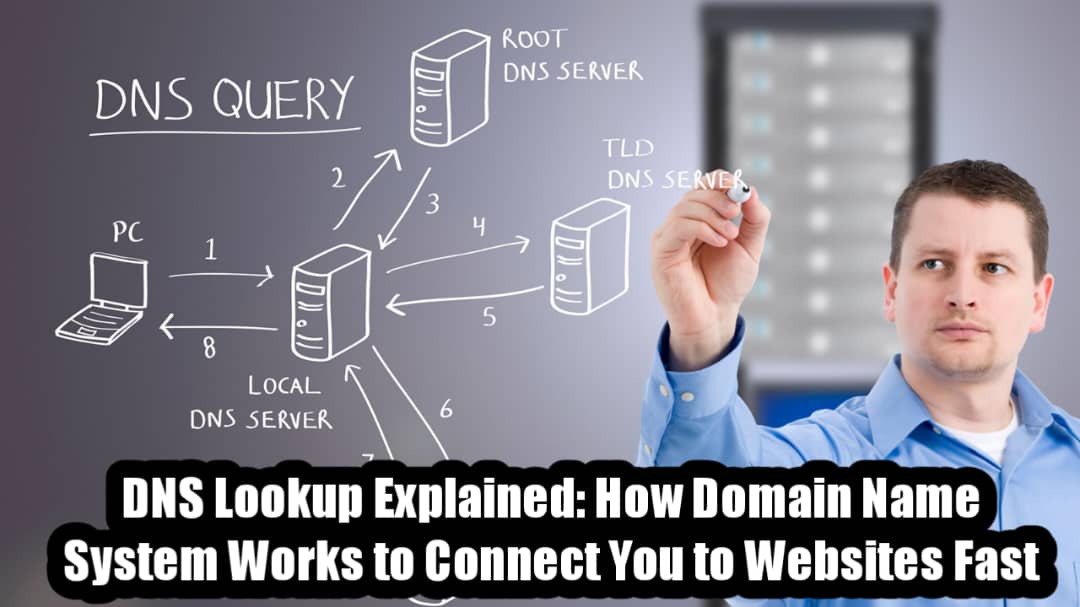
The DNS Lookup process involves several key steps and components. Here’s how it happens behind the scenes:
User Request:
When you enter a domain name in your browser, your system first checks if the IP address is already stored in its cache. If not, it initiates a DNS query.
Recursive Resolver:
The query is sent to a recursive DNS resolver, usually operated by your Internet Service Provider (ISP) or a public DNS like Google DNS (8.8.8.8) or Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1).
Root Name Server:
If the resolver doesn’t have the answer cached, it asks the root DNS server for the location of the Top-Level Domain (TLD) server, such as .com or .org.
TLD Name Server:
The resolver then contacts the TLD server to find the authoritative name server for the specific domain.
Authoritative Name Server:
This server holds the actual DNS records and returns the correct IP address to the resolver.
Connection Established:
Finally, the resolver sends the IP address back to your browser, which connects to the website’s server, and the page loads almost instantly.
This entire process usually happens in milliseconds, allowing users to access websites smoothly.
Types of DNS Lookups
There are two main types of DNS Lookups:
Forward DNS Lookup:
Converts a domain name into an IP address (the most common type).
Reverse DNS Lookup:
Converts an IP address back into a domain name, often used for email verification and network troubleshooting.
Why DNS Lookup Matters for SEO and Performance
DNS Lookup speed plays a significant role in website performance and SEO rankings. A slow DNS response can delay page loading time, affecting user experience and increasing bounce rates. Using fast DNS providers, caching, and Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) can drastically improve lookup times.
Additionally, ensuring your DNS records (like A, AAAA, MX, and CNAME) are properly configured helps maintain domain reliability and email deliverability.
Conclusion
DNS Lookup is a vital part of how the internet functions — silently ensuring users reach the right websites in milliseconds. By understanding how DNS works and optimizing DNS performance, website owners can achieve faster load times, better SEO results, and improved user satisfaction.